Search engines become smarter all the time. Google is constantly
improving its algorithms in order to give users the highest quality
content and the most accurate information.
Algorithms follow rules. Uncovering those rules – and taking advantage
of them – has been the goal of anyone who wants their website to rank
highly. But when Google finds out that websites owners have been
manipulating the rules, they take action, by issuing those websites with
a penalty. The penalty usually means a drop in rankings, or even an
exclusion from Google’s index.
As a website owner you sometimes know which rule you’ve broken. But for
many it’s hard to work out. Read our guide below to find out where
you’ve gone wrong and what you can do about it.
Table of contents
- Buying or selling links that pass PageRank
- Excessive link exchange
- Large-scale article marketing or guest posting campaigns
- Using automated programs or services to create links
- Text advertisements that pass PageRank
- Advertorials or native advertising where payment is received for articles that include links
- Links with optimized anchor text in articles or press releases
- Low-quality directory or bookmark site links
- Keyword-rich, hidden or low-quality links embedded in widgets
- Widely distributed links in the footers or templates of various sites
- Forum comments with optimised links in the post or signature
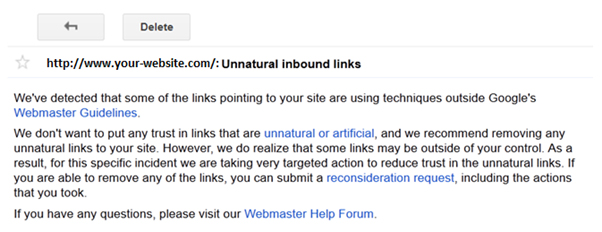
What is a Google penalty?
Google has been tweaking and improving its ranking algorithms since end
of year 2000. That’s when it released its toolbar extension and when PageRank was released in a usable form.
Since then, Google continued to work on the quality of search results it
showed to users as a result of their search queries. With time, the
search engine giant began to remove poor quality content in favour of
high quality, relevant information which it would move to the top of the
SERPs. And this is when penalties started rolling in.
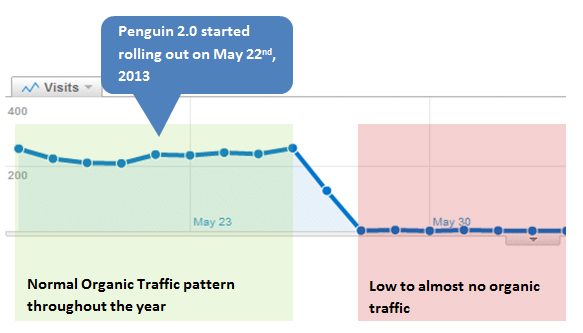
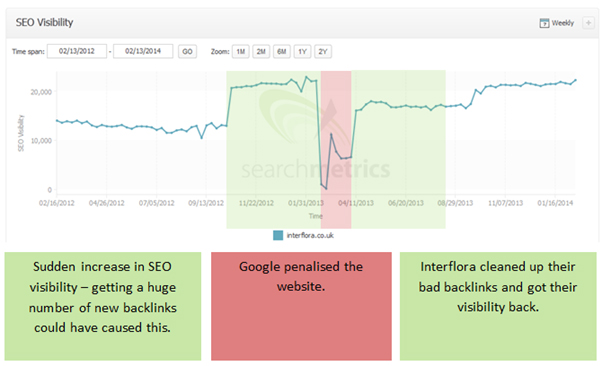
Next was the Penguin update which was rolled out in 2012 and hit more
than 1 in 10 search results. These algorithm changes have forced site
owners to rethink their SEO and content strategies to comply with
Google’s quality requirements.
How to tell if you’ve been penalised
To discover the reasons you might have been penalised, you can watch this video and skip to the next section, or just keep reading.
A penalty can be either automatic or manual. With manual penalties,
you’ll probably be notified that you’ve been doing something wrong that
needs to be fixed as soon as possible.
However, if the cause is a change of the algorithm, you may not always know you’ve been targeted.
Here are some clues you’ve been penalised by Google:
- Your site isn’t ranking well not even for your brand name. That’s the most obvious clue as your site should always rank well on that one keyword.
- If you’ve been on page one of Google’s search results and are dropping to page two or three without having made any changes.
- Your site has been removed from Google’s cached search results from one day to another.
- You get no results when you run a site search (eg: site:yourdomain.co.uk keyword).
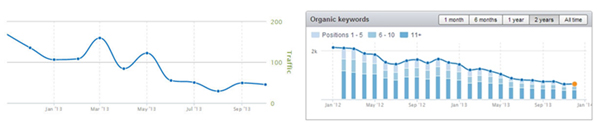
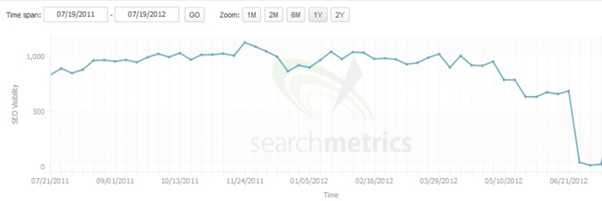
- You notice a big drop in organic traffic in your Google Analytics (or any other monitoring tool you’re using) especially a few days after a big Google update.
If you don’t have access to Webmaster Tools or Analytics, you can determine if you’ve been penalised by using one of the following tools:
- SEMRush – Check if your search engine traffic is decreasing every day and also if the total number of keywords ranking top 20 is starting to decrease quickly:
If you notice one or more of the above factors, then you can be sure
that Google has penalised your site and you need to do something about
it quickly.
What caused the penalty?
When dealing with a penalty, the first thing you need to do is try to
figure out what caused it – spammy links, over-optimising your content,
etc. Only then can you follow the steps to try to fix it.
The most common issue is having bad, low quality backlinks pointing to
your site. To find out what links Google considers to be “bad
backlinks”, check out Google’s Webmaster Guidelines on Link Schemes.
1. Buying or selling links that pass PageRank
These backlinks are considered one of the worst type of links and
they’re the main reason why many large websites have received a penalty.
Although money doesn’t necessarily have to exchange hands, a paid
backlink can also refer to offering goods or services in return for a
link back and even sending free products without specifically asking the
customers for a link back to your site.
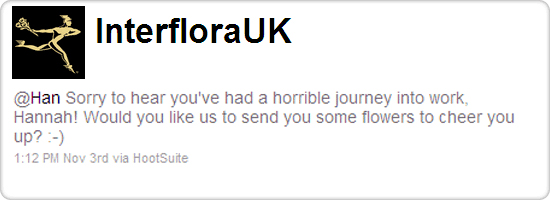
A good example of that is the Interflora incident.
The flower company sent out bouquets to make their customers feel better
after a hard day’s work. Happy to receive the surprise, some of the
customers wrote about the gesture on their own blogs/websites and linked
back to the flower company. While you’d think this was just a very nice
way of strengthening the relationship with their customers, Google
tagged it as a marketing technique of buying links and penalised
Interflora as a result.
2. Excessive link exchange
It’s common for company websites that are part of the same group to link
to each other. This is why Google declared war only on link exchange
done in excess. This is an old technique of getting backlinks as a
webmaster would get a backlink easier from a site owner if they also
returned the favour.
3. Large-scale article marketing or guest posting campaigns
There are numerous websites out there that are accepting article
submissions. So webmasters took advantage and started getting backlinks
by writing random articles and finding a way to add their own link.
However these articles were of very low quality which is why Google
decided to take action against those sites that were publishing articles
just for the sake of the backlinks.
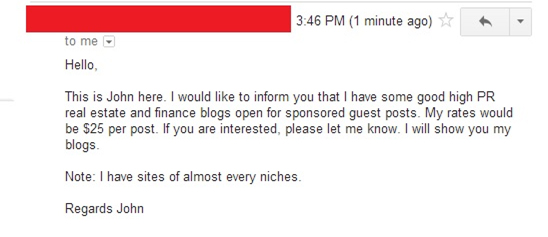
Guest blogging was recently added on the list of don’ts mainly because
it has quickly become a form of spam. Webmasters keep sending emails to
all sorts of websites asking to submit their articles in exchange for a
link. Sounds a lot like all the other spam email you never asked for but
keep receiving, doesn’t it? And it works the other way around too.
Webmasters that manage many blogs found guest blogging to be a good way
to make money:
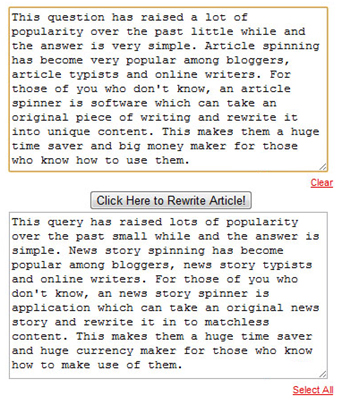
4. Using automated programs or services to create links
There are many tools used by black hat SEOs to create automated links,
such as ScrapeBox and Traffic Booster, but the most common tool is the
article spinner. In order to get content to add links, the spinner
helped webmasters get various pieces of content on the same subject
without having to pay someone to write them.
With such poor quality content around a link, it’s easy for Google to
realise this cannot in any way be considered a natural and earned
backlink.
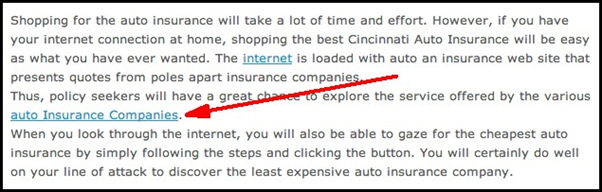
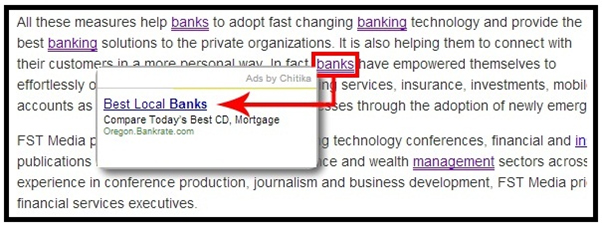
5. Text advertisements that pass PageRank
These types of links are created by matching a word to an advertisement.
In the example below, the article is about banks in general but when
you hoover over the word “bank” you get an ad to a specific business.
Since the presence of that business link is unnatural, this is one of the types of links that Google doesn’t like.
6. Advertorials or native advertising where payment is received for articles that include links
There are many websites out there filled with articles about various
products and each article has at least one link pointing to an
e-commerce website. The quality of the articles is rather low because
the sole purpose is to just create enough content around a link.
7. Links with optimized anchor text in articles or press releases
Similar to the previous one with the exception that instead of
contacting someone who has a website dedicated to building backlinks in
exchange for money, these links are added to articles and press releases
that get distributed over the internet through PR websites and free
article submission websites.
There are many wedding rings on the market. If you want to have a
wedding, you will have to pick the best ring. You will also need to buy
flowers and a wedding dress.
8. Low-quality directory or bookmark site links
Directories used to play an important role and represented an online
phonebook for websites. It was easier to find a website searching for it
by category. As search engine advanced, the need for these structured
directories decreased to the point where these are now being used for
link building purposes only.
9. Keyword-rich, hidden or low-quality links embedded in widgets
The best example is Halifax, the first bank that Google has hit. They
had these mortgage calculators embedded on various irrelevant websites
just for the backlink.
10. Widely distributed links in the footers or templates of various sites
Sitewide backlinks are to be avoided at all costs especially if the
links are on websites that are in no way related to your linked website.
If you place a link in the header, footer or sidebar of a website, that
link will be visible on all its web pages so don’t link to a website
that you don’t consider to be relevant for your entire content.
Most common footer links are either a web developer credit or a “Powered
by” link where you mention your CMS or hosting provider (see the
example below). There are also free templates out there that have a link
in the footer and most people never get that link out.
Sidebar links are usually Partner links or blogrolls. Since the word
“Partner” usually means that goods or services have been exchanged, this
can be considered a paid link so make sure to always use nofollow. As
for other related blogs, if they are indeed related, there should be no
issue but if your list has links to ecommerce websites or you’re using
affiliate links, you might want to nofollow those.
11. Forum comments with optimised links in the post or signature
Adding a signature link is an old link building technique and one of the
easiest ways of getting a link. It has also been done through blog
commenting. If you leave a comment on a forum or blog, make sure the
answer is not only helpful and informative but also relevant to the
discussion. If you add a link, it should point to a page that is also
relevant to your answer and the discussion.
Collecting the necessary data
Now that you know how to identify those bad links, let’s see how you can go about finding each and every one of them:
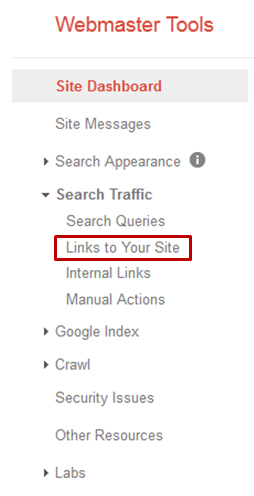
This is where Google shows you details on the backlinks it has indexed.
It should be your starting point in cleaning up your backlink profile as
it shows you how many backlinks each website is sending your way. This
is how you can find most of your site wide links – mark them down as
such.
2. Ahrefs, Majestic SEO, Link Detox, Open Site Explorer – Your choice
Depending on how many backlinks you have, you will probably need to pay for a good backlink checker tool.
Of course there are also free tools such as BackLinkWatch and AnalyzeBacklinks that you can use if you don’t have millions of backlinks in your profile.
The idea is to gather links from as many sources as possible as each
tool has its own crawler and can discover different backlinks. So, to
ensure you find as many as possible, it is indicated that you use
various tools.
Next get all the reports in one file, remove the duplicates and see how
many links you’re left with. You can sort the remaining links by URL
(coming from the same domain) to find the ones that are sitewide, by
anchor text (to find the exact-match anchors or “money keywords”) or by
any other type of data that those tools provide such as discovery date,
on-page placement and link type.
If you paid for links in the past or engaged in any of the link schemes
Google frowns upon, try to find all the websites that still have your
links by using a footprint. For instance, if you created website
templates that you’ve distributed for free but have added a “Created by
MyCompany” link in the footer, use the link’s anchor to find all the
websites out there that have used your template.
If you’ve got a penalty but haven’t paid for links or engaged in any of
the link schemes, check if your links might be considered spammy because
of the websites they’re found on.
Not sure what spammy links are? Well, there’s no better classifier than
your own eye so if you want to check a potential bad site your link is
on, ask yourself:
- Does the site look like spam – low quality or duplicate content, no structure, no contact page, loads of outbound links?
- Does your link and anchor text look like it belongs on the site?
- Are there toxic links on the site – Gambling, Viagra etc.?
- Does the site look like it sells links – e.g. loads of anchor text rich sidebars and site-wide links?
If the answer is yes to any of the above questions, then your link should not be there.
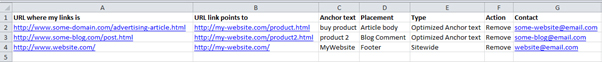
When you go through the links, try to take notes and write down as much information as possible for each bad backlink.
Contacting webmasters
When you’ve checked every bad link and have all the information you
need, start contacting every webmaster and ask them to remove or
nofollow your links. Keep a copy of the email threads for each website
as you will need to show proof that you have tried to clean up the bad
links.
If a contact email is not present on their site, look for a contact
form. If that is not available, try a WHOIS for that domain. If they’re
using private registration then just mark it down as a no contact.
To make the process easier and save some time, here are a couple of automated email tools you could use:
- rmoov (Free to $99/month) – This tool helps you identify contacts, created and sends emails, follows up with reminders and reports on results.
- Link Cleanup and Contact from SEOGadget (free) – Download the bad links from Google Webmaster Tools and upload them into the tool. SEOGadget then shows you the anchor text and site contact details (email, Twitter, LinkedIn).
- Remove’em ($249 per domain) – This solution combines suspicious link discovery with comprehensive email and tracking tools.
Be very persistent. If you’ve sent out emails and didn’t get a response,
send follow-up emails after a couple of days. Even if you’re desperate
to get the penalty lifted, keep in mind that those webmasters don’t owe
you a thing and unless you’re polite and patient, you’re not going to
get what you’re after.
Be organised. Create an online Google spreadsheet where you add your Excel list and also new columns to show:
- The date of the first email
- Response to first email
- Links Status after first email
- The date of the second email
- Response to second email
- Link Status after second email
- The date of the third email
- Response to third email
- Link status after third email
If you don’t get a reply from a webmaster after three emails, they’ll probably never reply so it might be time to give up.
Add a column for the email threads. Copy/Paste the entire email
discussion between you and a webmaster in an online Google doc and use
its link in your main worksheet. Make sure to set the Sharing options to
“Anyone with the link” so the Google Webspam team members can access
these documents.
When you’re done, your online document should look something like this:
The disavow file
After you’ve finished contacting all the websites, you’re now left with
the ones that haven’t replied, asked for money to remove the link or
with no contact details.
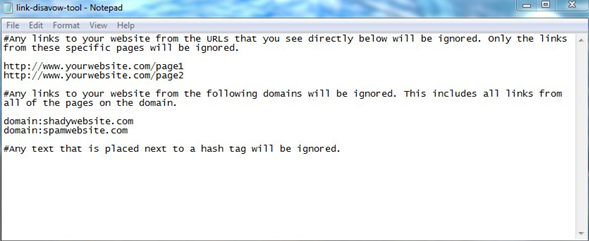
You should take these websites and add them to the disavow file.
You can add individual pages from a domain or the entire domain itself.
Since it’s not likely that a webmaster would create a bad link from one
page and a good link from another page pointing to your site, you’re
safer just disavowing the entire domain.
Use hashtags if you want to add comments such as:
# The owners of the following websites asked for money in order to remove my link.
# These are websites that automatically scrape content and they’ve also scraped my website with links and all.
# The webmasters of these websites never replied to my repeated emails.
URLs are added as they are and domains are added by using
“domain:domain-name.com” to specify that you’re disavowing all the links
that come from a specific domain.
This should be a simple .txt file (you can use Notepad). When you’re done, go to Webmaster Tools and upload it.
If you need to add more sites to an already submitted disavow file, you
will need to upload a new file which will overwrite the existing one –
so make sure the disavowed domains from your first list are also copied
in your second list.
Be very careful when using the disavow file. Don’t add full domains such
as WordPress or Blogger.com just because you had links from a subdomain
created on one of these platforms.
Also, add a domain to the disavow file only after you have tried your
very best to remove the link (and can show proof you’ve tried). Google
isn’t happy for you to renounce the link juice from certain websites, it
wants to see that you’ve also tried your best to clean up the internet
of all of your spammy links.
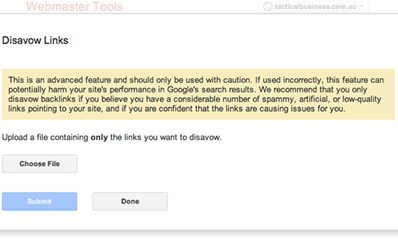
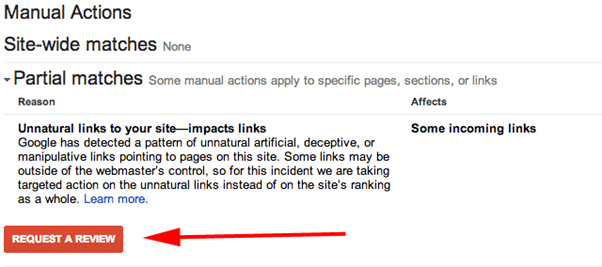
The Reconsideration Request
When you have the final status for every website that sent a bad link to
you and have also submitted your disavow file, it’s time to send Google
an apology letter also known as a Reconsideration Request.
You can do this from Webmaster Tools:
There is a 500 word and 2.850 character (including spaces) limit so use
this space wisely to explain what actions you’ve taken to try and clean
up your site.
Things that you should include:
- If you paid for links, then name the SEO agency you worked with to acquire links or any other similar information.
- What type of bad links you found in your profile such as sitewide links, comment spam and so on.
- What actions you’ve taken to make sure no more bad links will be created such as training employees to not buy or build links, retracting any free templates that had links in them, adding nofollow to the links in the widgets you provide.
- Link to the Google Online Spreadsheet where you’ve documented your efforts of contacting webmasters and taking down links. Make sure these documents are shared with anyone that has the link.
- Link to an online spreadsheet where you have a copy of the disavow file you’ve submitted.
- Confirmation of reading the Webmaster Guidelines, understanding them and following them from now on.
If you haven’t managed to clean up all your bad links, Google will reply
and give you examples of other bad links. You will then have to go
through the remaining links again using all the tools available and see
what other websites there are now after you’ve cleaned up most of the
other bad links.
Every month more than 400,000 manual actions are applied by Google and
every month the search engine giant processes 20,000 reconsideration
requests. Some of these reconsiderations are not the first ones sent out
by webmasters.
Don’t get discouraged if you don’t get your penalty removed on your
first try. Not many manage to do so. Just go back and repeat the process
until you manage to remove all the bad links from your profile.
How to avoid a future Google penalty
Even if your site hasn’t been penalised, don’t take a chance – go
through the guide and identify your bad links. You can follow every step
down to sending the Reconsideration Request. Since there’s no penalty
message, there is no need for this.
You can disavow the domains that are sending bad links to your site. You
should try to contact these websites first and always save every form
of communication you had with the webmasters.
If a penalty follows, you’ll already have proof that you’ve started to clean up your site.
For More Info about Penalised by Google? Here are 11 reasons why and how to recover