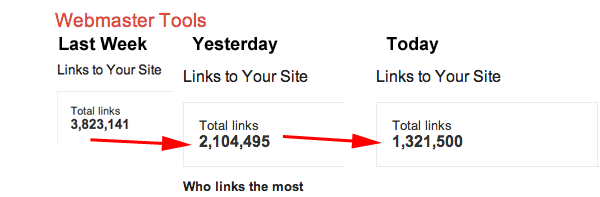
It has been an incredibly eventful year in terms of updates from Google. Major 2013 changes included further releases of Penguin and Panda, Hummingbird taking flight, and the shift away from providing keyword data thanks to encrypted search.
Many have gone so far as to ask whether SEO as a profession is dead: for one interesting perspective, see my recent Forbes interview with Sam Roberts of VUDU Marketing. My own take is less alarmist: Google has taken major spam-fighting steps that have shifted the playing field for SEO professionals and anyone trying to get their site on the map in the year ahead.
At the same time, the need for an online presence has never been stronger, while the landscape has never been more competitive. The potential to make a real ROI impact with your company's online marketing initiative is greater than ever. But defaulting to so-called "gray hat" tactics no longer works. Instead, SEO professionals need to step up and embrace a more robust vision of our area of expertise.
You might call it a move from tactician to strategist: the best and most successful players in our space will work to anticipate Google's next moves and respond to them with laser focus. In a sense, the infinite digital game of chess that is SEO will continue, but the rules of the game have become more complex.
Through a mix of what I'm observing and reading and what I'm seeing working out in the field today for my clients, here are some suggestions for companies and SEO professionals that are thinking ahead to 2014 for their digital strategies.
Everything You Learned in 2013 is Still Relevant, Just Amplified
When you look closely at the targets of the 2013 updates (ie, websites that cheat their way to the top of the rankings or provide no value to visitors), I anticipate seeing these carried forward throughout 2014. We can continue to expect micro adjustments to Panda and Penguin that continue to target both link quality and content quality.
When you look closely at the targets of the 2013 updates (ie, websites that cheat their way to the top of the rankings or provide no value to visitors), I anticipate seeing these carried forward throughout 2014. We can continue to expect micro adjustments to Panda and Penguin that continue to target both link quality and content quality.
Smart marketers will benefit from keeping a close eye on their link profiles, and performing periodic audits to identify and remove inbound links built unnaturally. High quality content investments will remain critical.
A solid SEO performance in 2014 is going to be built on a foundation of really understanding what happened in 2013, and what these changes mean both strategically and tactically for SEO. SEO really has changed in critical ways.
Content Marketing is Bigger than Ever
Content marketing will move from buzzword to mature marketing movement in 2014. From an SEO perspective, Google will be looking at companies that have robust content marketing efforts as a sign that they're the kind of business Google wants to support.
- Regular, helpful content targeted at your audience.
- Social signals from regular sharing and engagement.
- Freshness or signs that your site is alive and growing.
- Increasing authority connected to your body of work.
Sound familiar? It's the very approach to SEO that all of Google's recent updates have been designed to shape.
What changes you need to make in 2014 depends largely on where your company stands now in relation to an active content marketing strategy. Companies with existing content strategies will need to assess the role of mobile, specifically.
If you've just begun to move in the direction of content marketing, it's time to really commit and diversify. If you haven't started yet, it's time to take the plunge.
Social Media Plays an Increasingly Visible Role
Social media has been a major player in the digital marketing landscape for the last few years. First we saw the rise of mega platforms like Facebook and Twitter. In the last couple of years, visual content from networks like Pinterest, Instagram, and various micro-video services haa swept through.
Social media has been a major player in the digital marketing landscape for the last few years. First we saw the rise of mega platforms like Facebook and Twitter. In the last couple of years, visual content from networks like Pinterest, Instagram, and various micro-video services haa swept through.
Today, diversification is a major trend: depending on who you're targeting, it's no longer enough to be active on a single network. In fact, The
Content Marketing Institute recently released a study that the most successful B2B marketers are active on an average of seven networks. Companies and SEO professionals will need to be asking the following questions in the year ahead:
- Are we taking our social media seriously? Are we employing the pillars of strong profiles, good content, reciprocity, and engagement?
- Is easy social sharing enabled for all of our content?
- Does our content strategy include a dissemination phase that includes maximizing its potential for distribution through social networks?
- Are we active on the social networks that matter in our industry?
- Are we active on the social networks that matter to our customers?
- Are we active on the social networks that matter to the search engines? (See below for more thoughts on making that strategic investment).
- Does our social media marketing strategy stimulate the level of social signals required to achieve our goals?
Google's updates are likely to increasingly rely on social signals as active human curation of good content.
Invest in Google+
In addition to strengthening your overall social media marketing position, it's going to be absolutely critical that you are investing in your Google+ presence.
Moz's most recent study of
ranking factors confirms that Google+ is playing an increasingly significant role in a solid SEO ranking. The immediate areas to focus on include:
- Establishing Google Authorship of your content, and tying it to your Google+ account. Authorship, which brings your body of content together, will play an important role in the SERPs as well as strengthening your Author Rank.
- Those +1's add up. It isn't clear exactly how much Google +1's directly contribute, but it's fair to say that it's a major factor in the "social signals" component of Google's algorithm. I expect this to increase in the year ahead.
Hummingbird Was Just the Tip of the Mobile Iceberg
2014 will be the year of mobile SEO. Hummingbird was just the very small visible tip of a very large iceberg as Google struggles to respond to the rapidly shifting landscape where half of all Americans own smartphones and at least one-third own tablets. Those statistics will probably shift upward, maybe dramatically, after the 2013 holiday season.
As a result, your site's mobile performance matters to your SEO rankings. Properties that you're trying to rank need to be designed first for mobile and then scaled up for the big screen. If you don't have a mobile-optimized website, this needs to be your top priority in terms of SEO and design investments for 2014.
Some underlying changes that happened with Hummingbird, including the increasing importance of both semantic search and Knowledge Graph, will continue to grow in influence. Practically speaking, this is to help prepare the search engine for the rise of voice search associated with mobile. But it also has direct implications (which we're still learning about) for broader SEO. This is one area that you should pay close attention to, from how you structure your content to what content you choose to put out.
The Long Versus Short Debate
Which is better, long content or short content? The answer depends on who is creating the content, who is reading it, what it's about, in what context it's being consumed, and how you define "better."
For the purposes of this argument, which form of content will help you best prepare to rank well in 2014? Frustratingly for some, the answer is more "both/and" than "or."
Vocus recently cited a study that showed that the top 10 results for a specific keyword search tended to be more than 2,000 words in length. The validity of that study has been debated, but it's probably fair to say that length is a proxy for depth of expertise and value delivered to the reader.
Google values both expertise and value. As a result, we've seen a trend where the "minimum desirable length" for text-based content has shifted from something in the range of 550 words to articles in the range of 1000-plus words.
Yet we're also confronted with the reality of the mobile device: if I'm reading about something I'm only moderately interested in, there's a high probability that I won't want to scroll through 2,000 words on my iPhone. That leaves content marketers faced with the challenge of producing mobile-friendly content, which tends to be (in a sweeping generality) much, much shorter.
Proposed solutions have run the gamut from content mixes to site architectures that allow you to point readers to specific versions of content based on their devices. This is great for the user experience, but where it all comes out on the SEO algorithm front remains to be seen. For now, I'll just acknowledge that it's an area of concern that will continue to evolve and that it's something you should keep your eye on.
Advertising and PPC has a Shifted Relationship with SEO
Since Google made the decision to encrypt the vast majority of its searches, our ability to access keyword data for research purposes has been restricted. However, there's a loophole. Keyword data is still available for advertisers using PPC on Google's platform.
More SEO budgets may be driven toward PPC simply because access to the data may otherwise be restricted. It's also possible that we'll see the release of a premium Google product to give us access to that data through another channel from Google in the year ahead.
Guest Blogging Remains One of the Most Effective Tactics, With a Caveat
Guest blogging has exploded in the past year, and it's going to remain one of the most effective means of building quality inbound links, traffic, and branding exposure in 2014. However, it's absolutely critical that you're creating high quality content, and using extremely stringent criteria when selecting your target sites.
In other words, you need to apply the same high ethos approach to guest blogging that you do to the rest of your SEO efforts. If you dip a toe into spammy waters where guest blogging is essentially scattershot article marketing with a 2014 update, you're likely to be penalized in a future Penguin update.
Conclusion
This has been a year of significant change in the SEO industry. Even contemplating strategies for 2014 can feel staggering.
The good news is that looking back, it's easy to see which direction the trends are heading in terms of the years ahead. Staying the course on solid white hat tactics and paying attention to a few priority areas that are shifting rapidly should give you the insights needed to improve your organic search visibility in 2014 and beyond.
What trends do you anticipate seeing from Google in the year ahead? How are you preparing?